The latest research result of the team was published in Journal of Alloys and Compounds (IF=4.175).

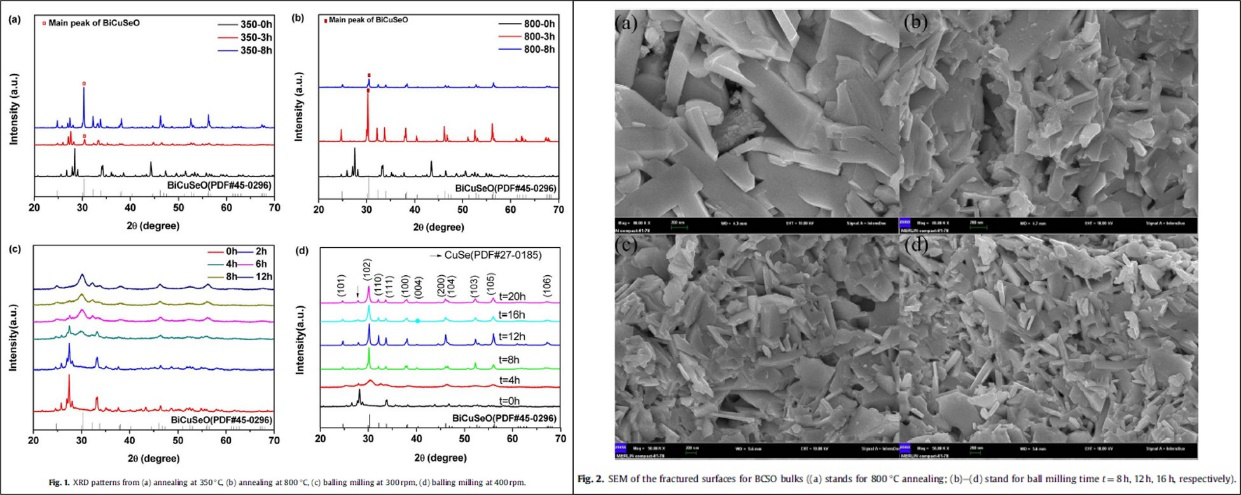
In this paper, the BiCuSeO based ceramics have been prepared by mechanical alloying (MA) and resistance pressing sintering (RPS) process. The effects of the parameters of annealing, ball milling and sintering on the microstructure, thermoelectric properties, and mechanical properties are investigated systematically. The results indicates that the samples prepared by MA exhibit higher carrier concentration due to higher Cu vacancies concentration, smaller grain size resulting in stronger phonon scattering, and correspondingly higher thermoelectric properties than those prepared by annealing. By prolonging milling time and increasing ball milling strength, it can further refine grains, increase the carrier concentration, enhance phonon scattering and further improve thermoelectric properties. Coupled with Ca/Pb doping, the electrical conductivity at room temperature increased to 445 Scm-1. The total thermal conductivity is below 0.90 Wm-1K-1 in the whole measured temperature range, which is attributable to the increased defects and gain boundaries. The maximum power factor of 0.75 mWm-1K-1 and ZT value of 1.15 were obtained for the Bi0.84Ca0.08Pb0.08CuSeO with BM time (t) = 16 h at 873 K.
Paper link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925838818316414?via%3Dihub
Paper: 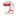 Effect of synthesis processes on the thermoelectric properties of BiCuSeO oxyselenides.pdf
Effect of synthesis processes on the thermoelectric properties of BiCuSeO oxyselenides.pdf
